ENEA Microbial Culture Collection
ENEA is involves as co-proponent in the research infrastructure "Strengthening the MIRRI Italian Research Infrastructure for Sustainable Bioscience and Bioeconomy" (SUS-MIRRI.IT), financed by Directorate Decree No. 114 of July 21, 2022, code N. IR0000005 of July 28, 2022, financed by NextGenerationEU within the framework of the National Recovery and Resilience Plan - Mission 4 "Education and Research", Component 2, "From research to enterprise", Investment Line 3.1 "Fund for the establishment of an integrated system of research and innovation infrastructure".
The SUS-MIRRI.IT project aims to strengthen the MICROBIAL RESOURCE RESEARCH INFRASTRUCTURE (MIRRI-IT) (http://www.mirri-it.it/), included in the list of Italian Research Infrastructures (RI) of high priority, in order to ensure the access to high-quality microbial resources preserved in the Culture Collections (CCs) associated with MIRRI-IT, resulting in the adaptation of Italian collections to international management standards to ensure the quality of the preserved material, a strategic aspect for increasing knowledge and the potential biotechnological and commercial exploitation of the microorganisms deposited therein. Biological resources (microorganisms, microbiomes, and their derivatives) are crucial for the advancement of biotechnologies, human health, agricultural and food systems, as well as for research and development in life sciences and bioindustry. Products derived from microorganisms (drugs, antimicrobials, biopesticides, biofertilizers, biomass, and industrial enzymes) are used in the production of all fermented foods, which are significant for the "Made in Italy" label, in the production of new superfoods and functional foods, in the formation of microbial consortia for sustainable agriculture, in bioremediation processes, and in the selection of microorganisms for the production of biofuels and new biomaterials.
The SUS-MIRRI.IT project aims to increase the biological resources stored at MIRRI-IT Research Infrastructure, improving their characterization and optimizing their management, thus unlocking their genomic and metabolic potential. The optimized management of microbial resources, combined with the construction of a digital platform and a data handling/sharing strategy, will lead to further scientific advances as well as the establishment of innovative solutions and products of biotechnological interest, favouring the bio-circular economy. Another objective is the creation of a network of Italian microbial resource centers as a key element for the scientific and biotechnological development of our country. The project idea is to establish a platform that enhances both known and unknown microbial biodiversity as a new resource for the development of bioeconomy and bioscience, focusing on sustainability and a true circular economy.
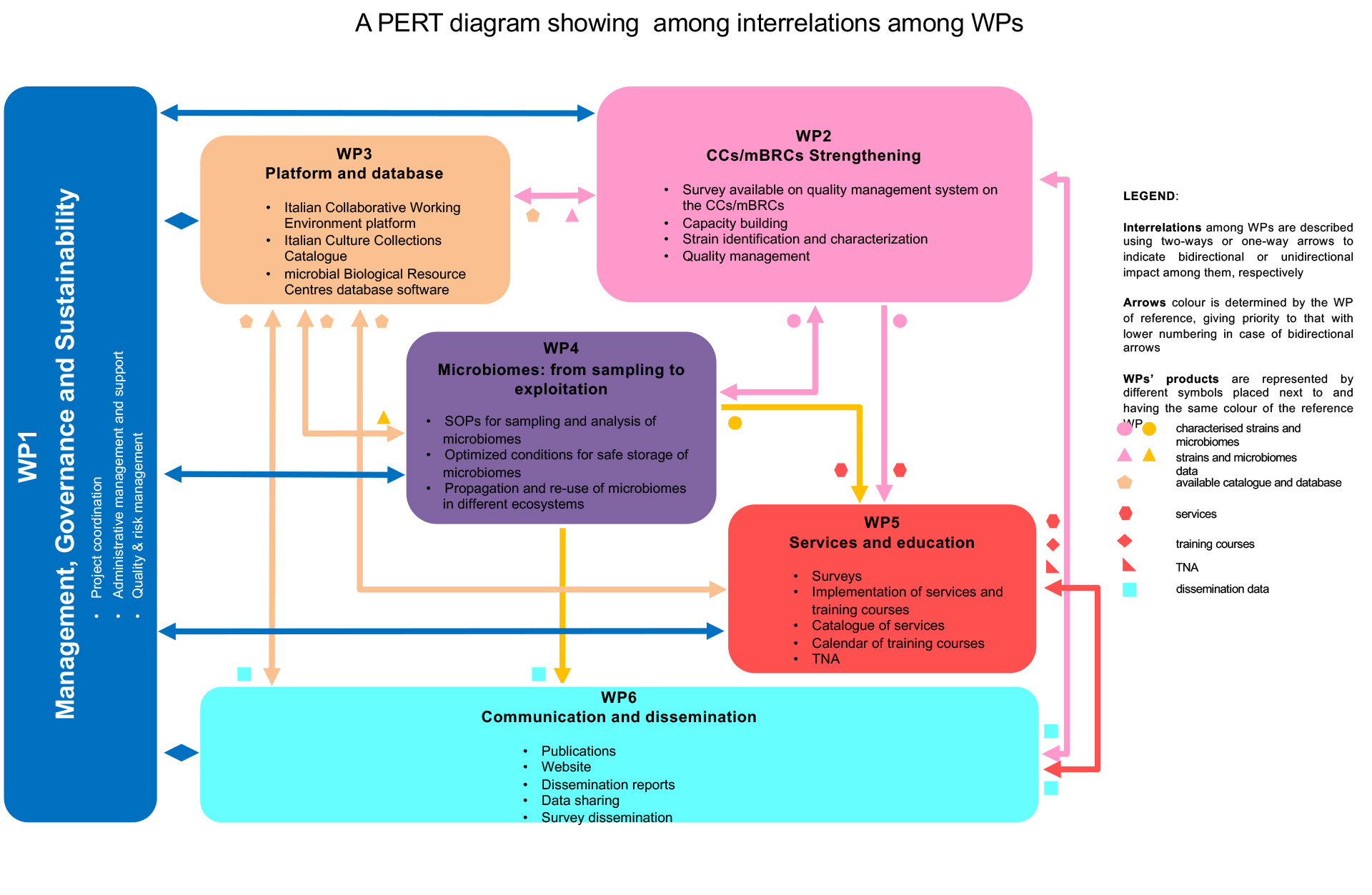
The project is structured into six Work Packages (WPs) as reported in Figure 1.
Fig. 1. Structure of project SUS-MIRRI.IT
The project is structured into the following 6 WPs:
- WP1 Management, Governance and Sustainability
- WP2 Culture collections (CCs)/Microbiological Resource Centers (mBRCs) Strengthening
- WP3 Platform and database
- WP4 Microbiome: from sampling to exploitation
- WP5 Services and education
- WP6 Communication and dissemination
SUS-MIRRI.It is coordinated by the University of Turin and involves 15 institutions with 24 OUs: University of Cagliari, University of Genoa, University of Milano Bicocca, University of Modena and Reggio Emilia, Federico II University of Naples, University of Palermo, University of Perugia, University of Parma, University of Sassari, University of Verona, and the University of Basilicata together with the OGS institute, CNR (with 7 Operating Units: ISA, IPSP based in Turin and Bari, IRSA, ISPA, IBBA, ICB) and ENEA (with 4 Operating Units: UO Casaccia, UO Brindisi, UO Portici, and UO Trisaia). The project is granted by the European Commission’s NextGenerationEU programme, with a total budget of about €17.000.000.